encounters an additional hurdle in the intes-
tinal mucosa and liver. The enzyme UDP-
glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) conjugates free
quercetin with glucuronide, a bulky and inert
adduct, hindering its functional dexterity and
cellular actions. Since the conjugate is easily
excreted, UGT also accelerates its systemic
clearance, limiting exposure of the flavonoid
to target tissues.2*
Quercetin is not alone in this tribulation, as
UGT wields a notorious predilection for
flavonoids and other polyphenols. In the
mid-1990s, researchers reported that piper-
ine, an alkaloid from black pepper, increased
the bioavailability of curcumin in both rats
and humans.10 More recently, piperine
enhanced the pharmacokinetic parameters of
resveratrol.11 It is now clear that piperine
effectively targets and moderates UGT.12
While more research is necessary to evaluate
the effects of piperine on quercetin action in
humans, preliminary evidence, published in
July 2013, indicates that piperine can
enhance the neurocognitive efficacy of
quercetin in mice.13*
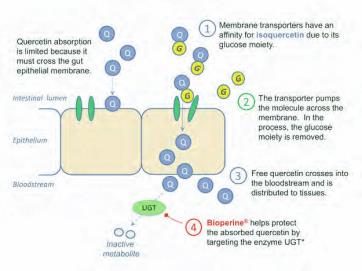
Figure 1. Quercetin bioavailability is
enhanced in two steps when isoquercetin
and piperine (Bioperine®) are combined:
First, isoquercetin, or glycosylated quercetin,
is absorbed more efficiently than free
quercetin due to its glucose moiety. During
absorption, the glucose is released, liberating
free quercetin into the bloodstream to access
tissues. Second, plasma quercetin is subject
to inactivation by the enzyme UDP-glu-
curonosyltransferase (UGT). Piperine
(Bioperine®) directly targets this enzyme to
maximize the durability of quercetin in the
body.*
Collectively, the evidence supports that iso-
quercetin offers rapid absorption and superi-
or overall bioavailability. Since the sugar
moiety serves merely as a delivery vehicle, its
therapeutic profile is identical to quercetin.
Modeled after nature's example, isoquercetin
is an excipient-free approach to bioavailabili-
ty enhancement. Isoquercetin w/Bioperine®
delivers isoquercetin in combination with
longer-acting rutin, together with clinically
researched Bioperine® piperine to maximize
clinical efficacy.*
References
1. Bischoff SC. Quercetin: potentials in the pre-
vention and therapy of disease. Curr Opin Clin
Nutr Metab Care (2008) 11(6):733-740.
7. Gee JM, DuPont MS, Day AJ, et al. Intestinal
transport of quercetin glycosides in rats involves
both deglycosylation and interaction with the hex-
ose transport pathway. J Nutr (2000)
130(11):2765-2771.
8. Olthof MR, Hollman PC, Vree TB, Katan MB.
Bioavailabilities of quercetin-3-glucoside and
quercetin-4'-glucoside do not differ in humans. J
Nutr (2000) 130(5):1200-1203.
9. Erlund I, Kosonen T, Alfthan G, et al.
Pharmacokinetics of quercetin from quercetin agly-
cone and rutin in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin
Pharmacol (2000) 56(8):545-553.
10. Shoba G, Joy D, Joseph T, et al. Influence of
piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in
animals and human volunteers. Planta Med (1998)
64(4):353-356.
11. Johnson JJ, Nihal M, Siddiqui IA, et al.
Enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol by com-
bining it with piperine. Mol Nutr Food Res (2011)
55(8):1169-1176.
12. Srinivasan K. Black pepper and its pungent
principle-piperine: a review of diverse physiologi-
cal effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr (2007)
47(8):735-48.
13. Rinwa P, Kumar A. Quercetin along with
piperine prevents cognitive dysfunction, oxidative
stress and neuro-inflammation associated with
mouse model of chronic unpredictable stress. Arch
Pharm Res (2013) Jul 16. Advance Online
Publication. DOI 10.1007/s12272-013-0205-4.
*These statements have not been evaluated
by the Food & Drug Administration. These
products are not intended to diagnose, treat,
cure or prevent any disease.
Isoquercetin w/Bioperine®, 60 capsules
from Pure Encapsulations, is available at
Willner Chemists.
100 Park Ave or 253 Broadway, NY NY
or www.willner.com.
Page 36
The Willner Window Product Reference Catalog, Winter 2014
since 1911
• Willner Chemists •
the nutritional supplement professionals
Phyto-Tech™ Menopause Complex (for Menopausal symptoms)
Phyto-Tech™ Fertility Complex (if infertile, trying to become preg-
nant)
Phyto-Tech™ Dong Quai Root (if estrogen deficient)
Phyto-Tech™ Black Cohosh Root (for hot flashes, cramps)
1 fl oz - Prod Code: 56989
Chinese Red Ginseng
Chinese Red Ginseng
Ginseng is the premier adaptogenic, immune-modulating herb.
Chinese Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng) is more “stimulating” or
warming than American Ginseng.
Who would benefit from this supplement? Those suffering from
fatigue, burn-out, frequent illness, depression. Red Chinese Ginseng
is thought to increase vigor, energy, vitality and resistance to illness
and environmental or external stress. It is often the preferred adap-
togenic herb for the elderly.
Supplemental Information:
Phyto-Tech™ Chinese Red Ginseng increases vigor, energy, vitality
and resistance to illness and environmental stresses. It is best for
those who are depleted and are low on passion in life. It is also
indicted for those working too hard and are afraid of burn out. Red
Chinese Ginseng will increase the stress hormone ACTH from the
pituitary that helps the body adapt to stress. When stress is initiating
the breakdown on one’s innate weakness (genetic, constitutional,
predispositional tendencies), Red Chinese Ginseng will help the
body to cope and therefore assist in many chronic diseases, especial-
ly if debilitating and wasting.
Phyto-Tech™ Chinese Red Ginseng is not for those in their prime
of life who are full of fire, the Type-A personality. It is for those who
used to be that way and are now not what they used to be. It helps
in the aging process to stay alert, youthful, energetic and adaptive to
environmental changes. It is immunomodulating and keeps the
immune system firing on all levels.
Phyto-Tech™ Chinese Red Ginseng is a tonic for the 21st century
with the fast paced life style that creates accelerated wear and tear.
It gives more mileage to the body.
Phyto-Tech™ Chinese Red Ginseng should be considered for
depression in the elderly who might not be chemically depressed in
a St. John’s Wort way (serotonin), but need some energy to process
life with more passion and enjoyment. It is synergistic with Ginkgo
for the elderly.
Phyto-Tech™ Chinese Red Ginseng is a more yang or warming and
stimulating ginseng than the American. Eleuthero Root (sometimes
referred to as Siberian Ginseng) is not a true Ginseng and is consid-
ered neutral, not warming or cooling.
Phyto-Tech™ Chinese Red Ginseng contains 333 mg of imported
Chinese Red Ginseng per 30 drops.
Dosage: 15-45 drops, 2-3 times per day It is best used as a long
term tonic (1-3 months and longer).
1 fl oz - Prod Code: 57023
Chlorophyll Extract
Chlorophyll Extract
Often considered the “blood” of plants, chlorophyll is structurally
similar to hemoglobin. It has a protective and detoxifcation
action.
Who would benefit from this supplement? Those with heavy metal
toxicity and those looking for cleansing and detoxification properties.
Those with bad breath and body odor. Those suffering from fatigue
and those with slow healing wounds.
Phyto-Tech™ Chlorophyll provides 100 mg Chlorophyll, from
Mulberry leaf, per 30 drops.
Dosage: 15-30 drops in water or juice, 1-2 time daily, or as need-
ed
Supplemental Information:
Chlorophyll is the sunlight collecting molecule in plants that gives
them their green pigment. Plants use chlorophyll to collect light
needed for photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis Chlorophyll mol-
ecules have the ability to convert solar energy into chemical energy
by manufacturing carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water.
Chlorophyll is often referred to as the “blood” of plants.
Interestingly, Chlorophyll molecules are structurally very similar to
human hemoglobin molecules. The difference between the two
being that Chlorophyll carries Magnesium at its center and hemoglo-
bin carries iron at its center. Like iron, Chlorophyll helps the body
build red blood cells and thus increases oxygen availability. It ener-
gizes and revitalizes the body and is helpful for fatigue, shortness of
breath, asthma, altitude sickness and intense physical exertion.
Chlorophyll acts as an internal deodorizer and is helpful for people
with halitosis (bad breath) and body odor. It can be used as an aid to
reduce digestive tract odor from a colostomy or ileostomy and also
fecal odor caused by incontinence. It can also help for foul smelling
gas. Chlorophyll cleanses and nourishes the intestinal tract and is
healing to the mucosal lining. It can also be helpful for constipation.
Chorophyll is an excellent whole body cleanser. It not only detoxi-
fies the digestive tract, but also facilitates cleansing of the blood and
liver and assists in the chelation of heavy metals. It is capable of neu-
tralizing harmful oxidants and may reduce oxidative damage from
certain carcinogens. It also has the ability to form tight molecular
complexes with carcinogens and in doing so blocks the body’s
absorption of them. In a placebo controlled study conducted in
China Chlorophyll supplementation was found to decrease DNA
damage caused by aflatoxin, a liver carcinogen produced by fungus
in moldy grains and legumes. Scientists hope that in populations
with unavoidable dietary aflatoxin exposure Chlorophyll supplemen-
tation could significantly reduce the risk of developing liver cancer.
1 fl oz - Prod Code: 56977
Cinnamon Bark 40
Cinnamon Bark 40
This is a standardized Cinnamon Bark complex in a liquid filled
veggie cap.
Historically, Cinnamon has been used for various gastrointestinal
problems. More recently, interest has centered on the research
showing that Cinnamon can help normalize blood sugar control.
This is of major interest to those with type 2 diabetes.
Who would benefit from this supplement? Those with blood sugar
regulation problems, including type 2 diabetes, pre-diabetes, and
cholesterol related conditions.
Each two liquid filled veggie caps contain 250 mg of Cinnamon
Bark (alcohol extract), 75 mg of Cinnamon Bark (supercritical carbon
dioxide extract, standardized ro 40 mg Cinnamaldehydes.
According to Natural Standard Integrative Medicine database,
“Cinnamon may be used for various medical conditions (77;?78). In
a survey of parents in Germany determining the use of complemen-
tary and alternative medicines in children with type 1 diabetes in
four pediatric diabetes centers (located in Leipzig, Berlin, Stuttgart,
and Bonn), 5.6% reported using cinnamon for this indication (79).
Cinnamon has been touted as having a positive effect on postprandi-
al glucose metabolism (80). Its ability to lower blood sugar in individ-
uals with diabetes has been discussed (81). Naturally occurring com-
pounds found in cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia), including chromi-
um and polyphenols, may improve insulin sensitivity (82). Human
data suggest that cinnamon exhibits "sweet" properties and may be
used in strategies for reduction of sugar intake (83).
Each two liquid filled veggie caps contain 250 mg of Cinnamon
Bark (alcohol extract), 75 mg of Cinnamon Bark (supercritical carbon
dioxide extract, standardized ro 40 mg Cinnamaldehydes.
Also available in a vegetarian capsule form. Each veggie capsule
contains 410 mg of certified organic Cinnamon Bark.
The Cinnamon used in Phyto-Tech™ Cinnamon supplements is
Cinnamomum cassia, the species utilized in research. It is certified
organic and vegetarian.
60 Liquid Filled Capsules - Prod Code: 57092
90 Veggie Caps - Prod Code: 60118
Cleanse Complex 1:2
Cleanse Complex 1:2
A herbal formula based on traditional concepts of a rapid,
systemic (full body) cleansing.
. . . continued on page 38
Important Notice: The information given here is designed to help you make informed decisions about your health, and the proper use of dietary supplements. It is
not intended as a substitute for medical advice, nor a substitute for any treatment that may have been prescribed by your doctor. If you have a medical problem, you
should seek medical help. Products described herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or mitigate disease.
Product Reference Guide: Willner Chemists Phyto-Tech™ Herbal Supplements
. . . continued from page 32
2. Heim K, Tagliaferro AR, Bobilya DJ. Flavonoid
antioxidants: chemistry, metabolism and structure-
activity relationships. J Nutr Biochem (2002)
13(10):572-584.
3. Ueno I, Nakano N, Hirono I. Metabolic fate
of [14C] quercetin in the ACI rat. Jpn J Exp Med
(1983) 53(1):41-50.
4. Hollman PC, van Trijp JM, Mengelers MJ, et
al. Bioavailability of the dietary antioxidant flavonol
quercetin in man. Cancer Lett (1997) 114(1-
2):139-140.
5. Hollman PC, van Trijp JM, Buysman MN, et
al. Relative bioavailability of the antioxidant
flavonoid quercetin from various foods in man.
FEBS Lett (1997) 418(1-2):152-156.
6. Manach C, Morand C, Demigné C, et al.
Bioavailability of rutin and quercetin in rats. FEBS
Lett (1997) 409(1):12-16.
Figure One